Air curtain or airwall: What are the differences?
When it comes to sealing off doors and gates, there are two relevant options: Air curtains or air walls. In principle, both technologies are similar, but there are significant differences. Which system is best suited for which application depends on several factors.
Air curtains and air walls are ventilation and air conditioning systems. Unlike other air handling units, such as humidifiers, dehumidifiers or filters, air walls and air curtains usually seal off a room from outside air. Both have different areas where they are used: Door air curtains, door air curtains or an air curtain are used for doors and smaller gates. Air walls, also called air curtains, are mainly suitable for large entrances, but smaller units can also seal off normal doors and even refrigerated trucks. The differences in technology result in different uses and advantages.
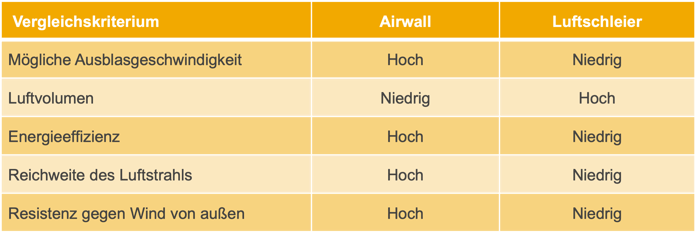
Airwalls and air curtains: a compact comparison
Airwall versus door air curtain: a head start through flow technology
Airwalls and air curtains differ in their functional principle primarily in two aspects: While air curtains accelerate a lot of air volume to a low velocity in order to seal entrances, airwalls are characterised by a higher air velocity but move less air in return. As a result, airwalls can reliably seal significantly larger gates, work more energy-efficiently and are more versatile.
This is achieved by pressure modules in which significantly higher pressure is built up than in air curtains, as well as a fluidically optimised design so that this pressure is efficiently converted into speed. This is achieved by patented nozzles that produce a precise, laminar and narrow air jet.
Energy efficiency: Airwall beats door air curtains
Airwalls are particularly distinguished by their energy efficiency. When door air curtains are operated for long periods or around the clock, energy consumption, costs and CO2 emissions are relevant factors.
The difference becomes most obvious when the system is used to distribute warm air at entrances in order to regulate the temperature at the workplace. Due to the high air volume, air curtains consume considerably more energy for this than airwalls, because more mass has to be heated and blown out. With airwalls, a built-in heating coil needs to heat less air and is therefore more energy-efficient.
Today, planners for technical building equipment (TBE) must place energy efficiency at the centre of their considerations. The most urgent issue is to keep unwanted air out of air-conditioned buildings. That is why, above all, incoming air – draughts – must be prevented across the entire cross-section of a door. Airwalls are designed for this and are much better at ensuring different air environments. This keeps out cold in winter and heat in summer.
"Because of the clean separation between warm and cold air, colleagues near the airwall have one of the coolest workplaces in summer and one of the warmest in winter."
Harald Schillinger, Senior Manager Maintenance and Sales Development, OBI Germany
When possible, airwalls can also use waste heat from machines and warm air under the ceiling to become even more efficient. The innovative technology in airwalls thus directly supports the achievement of climate targets.
Nevertheless, many companies – especially in retail – rely on air curtains. For smaller entrances and doors, these installations can suffice. But in terms of size, scalability and efficiency, air walls are clearly superior to the widely used air curtains, which makes them ideal for industrial purposes in particular.

Energy efficiency in air-conditioning technology through the use of airwalls
- Reduction in energy consumption of up to 450MWh per year
- Increasing energy efficiency
- Contribution to climate neutrality in Europe
Read our case study on energy efficiency now and find out how the flower wholesale market in Cologne saves up to 600 MWH annually.
Installation, adaptability and versatility
In terms of possible installation locations, airwalls offer significantly more flexibility than air curtains. Airwalls are modular, so they can be retrofitted into most buildings without conversion. Likewise, different modules can be combined to form individual installations, for example to cover particularly large or wide entrances. It is also possible to seal off several entrances with just one system.
Air curtains, on the other hand, are usually fixed systems that are available in different widths but are not modular and thus cannot be adapted to on-site requirements. This makes them difficult, especially for industrial purposes. Their mode of operation also prevents efficient use for entrances with large heights. This limits their usability for companies with large production buildings, logistics halls or high-bay warehouses.
Where airwall systems are used
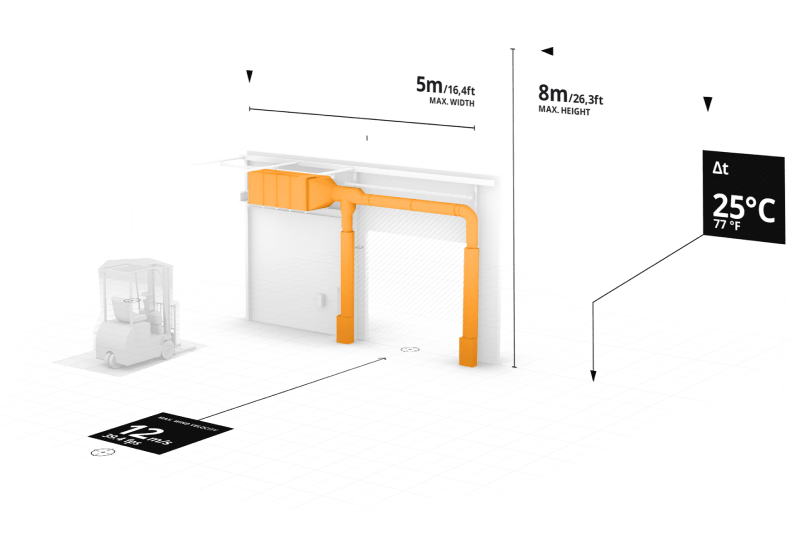
Airwalls are used, for example, in buildings to separate different temperature zones. The cold air from refrigerated warehouses remains with the systems in the rooms where products and goods are to be cooled. For a well-known international battery manufacturer, LWT Airwalls designed a special air wall that reliably keeps the temperature 25 degrees Celsius above ambient. This enables the company to shorten transport routes and use autonomous logistics vehicles. This is only possible thanks to the special technology in airwalls. Together with renowned research institutes such as the Fraunhofer Institute, LWT Airwalls is also constantly developing its systems further.
But not only warm or cold air is reliably kept out: Airwalls fulfil the requirements of the Federal Immission Control Act. They keep out fine particles, dust, odours and gases, so that they may also be used for mechanical-biological plants in the disposal of recyclable materials. Numerous systems are in operation and reliably protect employees at waste disposal companies.
Airwall systems also reliably keep insects out. The scientifically confirmed protection is an advantage in food production, among other things: when goods have to be loaded, the passageways can remain barrier-free without the fear of insects entering.
These are just three examples of the versatile areas of application for airwalls. On our website we present numerous other practical examples for which airwalls are suitable.
